For elderly individuals, maintaining mobility is essential for both independence and overall health. Walkers are one of the most effective tools for providing extra support, stability, and confidence while walking. But with so many types available, it can be hard to know which walker will meet their needs best. Here’s a complete guide to selecting the right walker, covering types, features, and key considerations to help ensure safety and comfort.
Benefits of a Walker for the Elderly
Walkers provide essential support to elderly individuals by:
- Improving Stability and Balance: Walkers help reduce the risk of falls by providing a sturdy support to lean on.
- Promoting Independence: With a walker, seniors can move more confidently on their own, allowing them to participate in daily activities without as much assistance.
- Relieving Pressure on Joints: For those with arthritis or joint pain, walkers help distribute weight and relieve stress on the knees and hips.
- Building Strength: Walkers allow seniors to maintain an active lifestyle, which can improve muscle tone and strength over time.
Types of Walkers for the Elderly
Each type of walker offers different levels of support and mobility. The choice depends on the senior’s specific needs, activity level, and any mobility challenges they face.
- Standard Walker (No Wheels)
- Best For: Those needing maximum stability and minimal mobility.
- Features: Standard walkers have four solid legs with rubber tips. Users lift the walker, move it forward, and take a step, making it ideal for those with balance issues but requiring some upper body strength.
- Two-Wheel Walker
- Best For: Seniors needing moderate stability but also wanting ease of movement.
- Features: This walker has two front wheels and two rear legs with rubber tips. The wheels help users push the walker without lifting it completely, making it easier to use and providing good support.
- Three-Wheel Walker
- Best For: More mobile seniors who need support but want maneuverability.
- Features: A compact, triangular-shaped walker with one wheel in the front and two in the back. This type of walker is easy to turn and navigate, particularly in tight spaces, but may lack the full stability of a four-wheel walker.
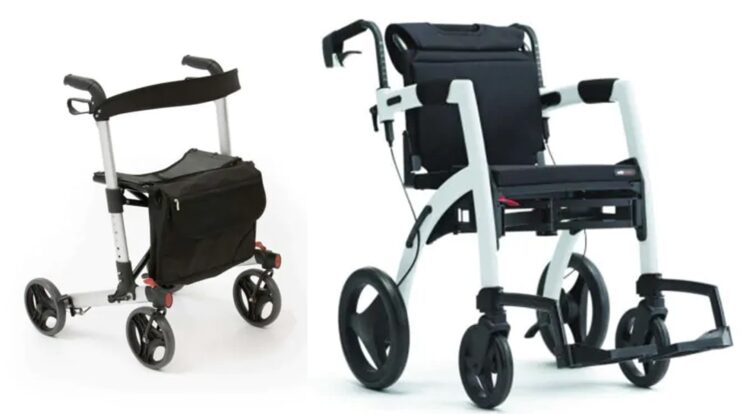
- Four-Wheel Walker (Rollator)
- Best For: Active seniors needing support for longer distances.
- Features: Rollators come with four wheels, hand brakes, and often a built-in seat for resting. This type of walker is highly maneuverable and ideal for seniors who need some support but are still fairly mobile.
- Knee Walker
- Best For: Individuals with injuries or conditions that prevent weight-bearing on one leg.
- Features: This walker has a knee pad where the injured leg rests while the person pushes with the uninjured leg. It’s often used as an alternative to crutches after surgery or an injury.
Key Features to Consider in a Walker
When choosing a walker, look for features that enhance safety, comfort, and ease of use.
- Adjustable Height: Walkers should be height-adjustable to allow for a comfortable, natural posture and to prevent hunching or stretching.
- Hand Grips: Padded grips reduce strain on the hands and wrists, making the walker more comfortable, especially for those with arthritis or joint pain.
- Weight Capacity: Check the weight limit of the walker to ensure it can support the user’s weight comfortably. Many walkers can hold up to 250-300 pounds, with bariatric models supporting even more.
- Brakes: For walkers with wheels, brakes are essential for safe stopping. Rollators often have hand brakes, which allow users to control movement and stop when needed.
- Folding Mechanism: If space is a concern, consider a walker that folds easily for storage or transport. This is especially helpful if the walker needs to be taken on outings or stored in a small space.
- Seat and Storage Options: Some walkers, especially rollators, come with built-in seats, which are helpful for those needing frequent rests. Storage compartments or baskets are also convenient for carrying personal items.
Safety Tips for Using a Walker
To ensure safety and effectiveness, seniors and caregivers should follow these tips:
- Proper Adjustment: Make sure the walker is set to the right height. The hand grips should align with the crease of the wrist when standing straight with arms at the sides.
- Use on Flat, Even Surfaces: Walkers work best on flat, even surfaces. Take caution when moving over uneven ground or steps.
- Engage Brakes When Stationary: If using a rollator, always engage the brakes before sitting down or stopping to prevent the walker from rolling.
- Lift or Adjust Carefully: For walkers that don’t roll, remind users to lift and move the walker forward carefully instead of dragging it, which can damage the walker and reduce stability.
- Consider Physical Therapy: If a senior is new to using a walker, sessions with a physical therapist can help them learn proper techniques and improve balance and strength.
How to Choose the Right Walker
- Assess Mobility Needs: Start by evaluating the individual’s mobility level and specific needs. Are they very mobile and simply need some support? Or do they need maximum stability?
- Consider Lifestyle and Environment: Think about where the walker will be used most. For outdoor use, four-wheel walkers (rollators) are often best. For tight indoor spaces, a three-wheel walker might be more suitable.
- Test for Comfort: If possible, try out different walkers to see which feels the most comfortable and natural to use.
- Look for Durable and Lightweight Materials: Aluminum walkers are durable and lightweight, making them easy to maneuver and transport.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: A doctor or physical therapist can help recommend the best walker based on specific needs, health conditions, and lifestyle.
Top Walkers for Elderly Individuals
Some popular and trusted brands of walkers for seniors include Drive Medical, Medline, Hugo, and NOVA. These brands offer a range of high-quality walkers, from standard models to advanced rollators with added features.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What’s the difference between a walker and a rollator?
- A walker typically has no wheels or two wheels, requiring the user to lift and move it forward. A rollator has four wheels, hand brakes, and often a seat, making it easier to maneuver but requiring a bit more control.
- How do I know if a walker is the right height?
- The walker is the correct height if, when standing straight with arms at the sides, the hand grips align with the crease of the wrist.
- Is a walker covered by insurance?
- In many cases, walkers are covered by Medicare or other insurance plans if deemed medically necessary. Check with the provider and get a prescription from a healthcare professional if needed.
In Summary
Choosing the right walker can make a significant difference in the quality of life for elderly individuals, allowing them to move confidently and maintain their independence. By understanding the types of walkers, key features, and safety tips, caregivers and seniors can find a walker that fits their needs and supports their active lifestyle. With the right support, staying mobile and independent becomes a much more achievable goal.